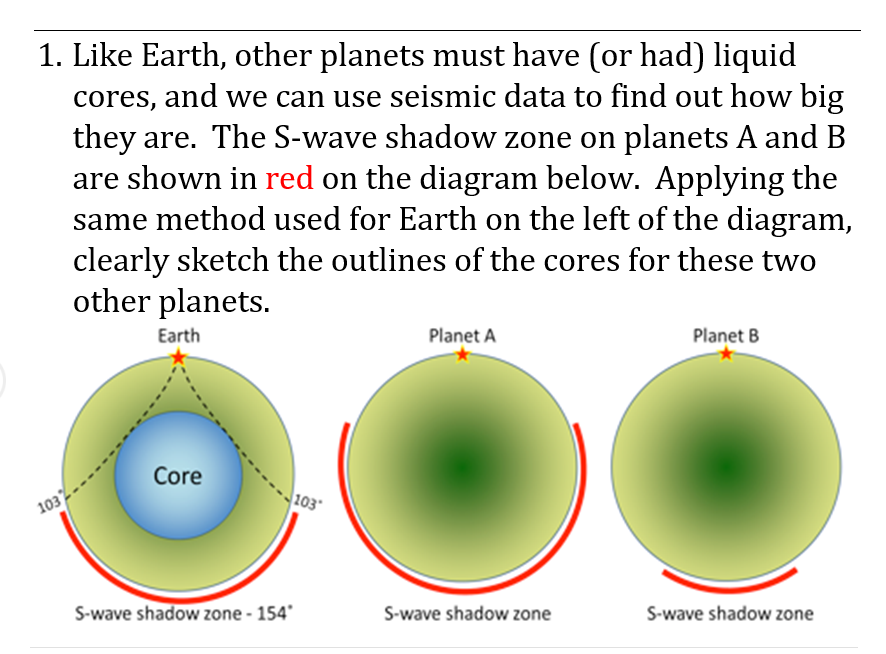
S Wave Shadow Zone Diagram
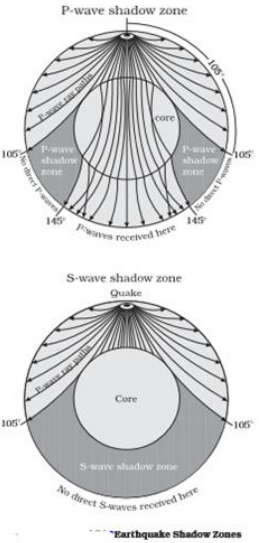
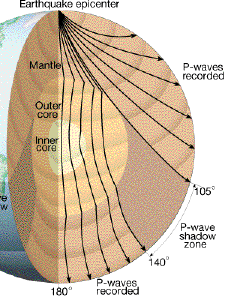
P-wave shadow zone P-wave shadow zone (from USGS ) Almost all the information available on the structure of the Earth's deep interior is derived from observations of the travel times, reflections , refractions and phase transitions of seismic body waves, or normal modes.
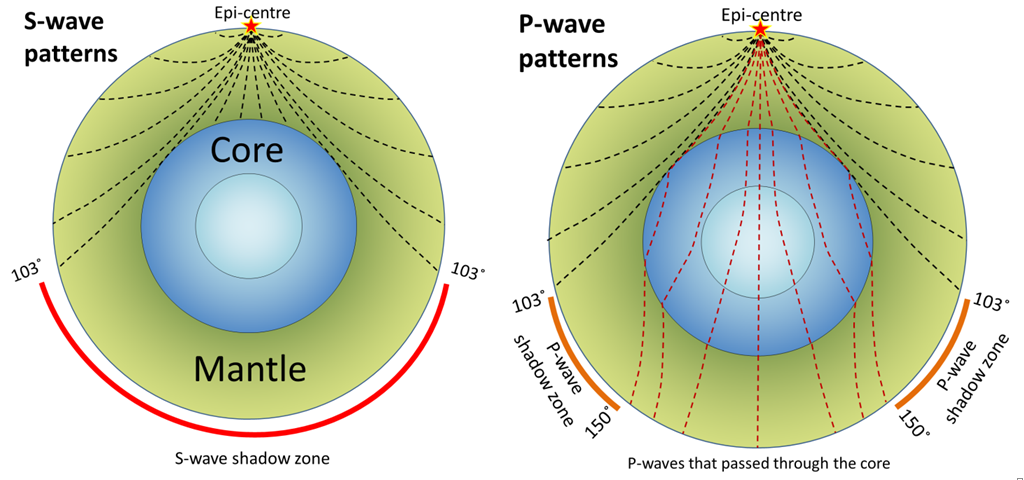
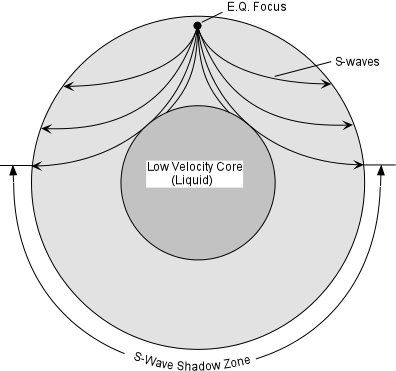
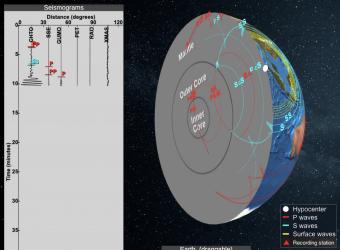
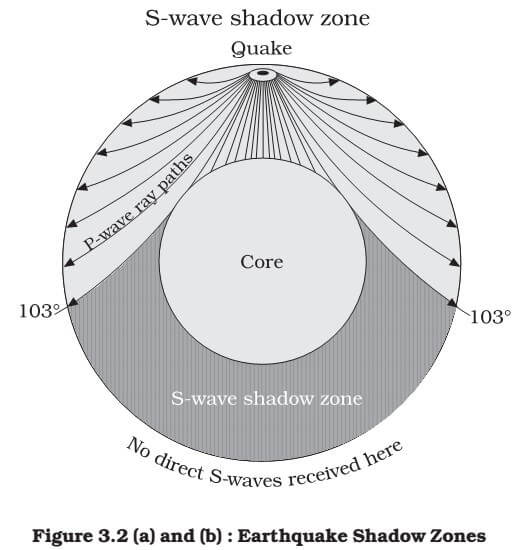
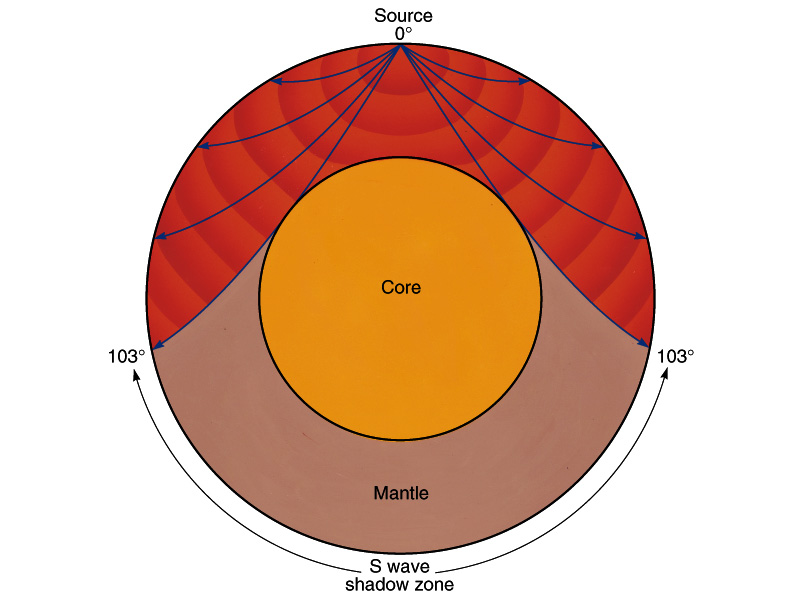
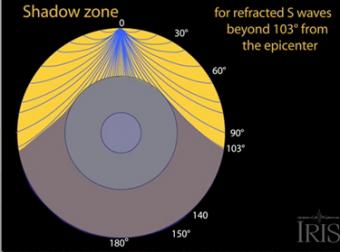
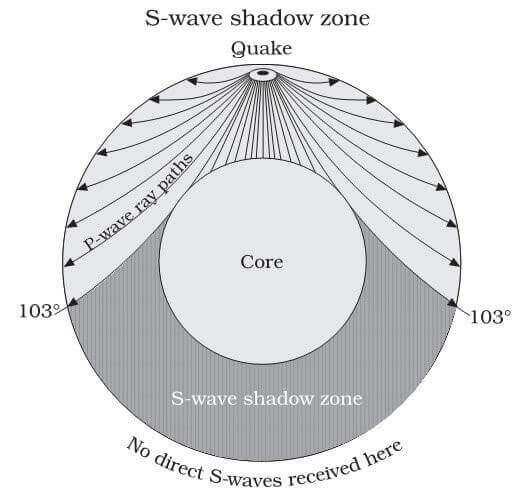
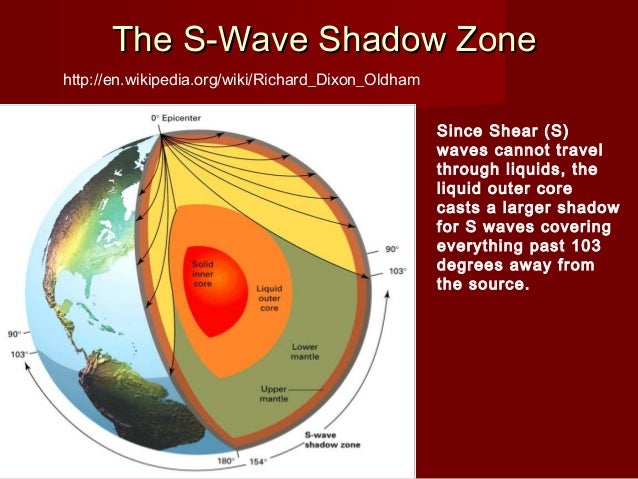
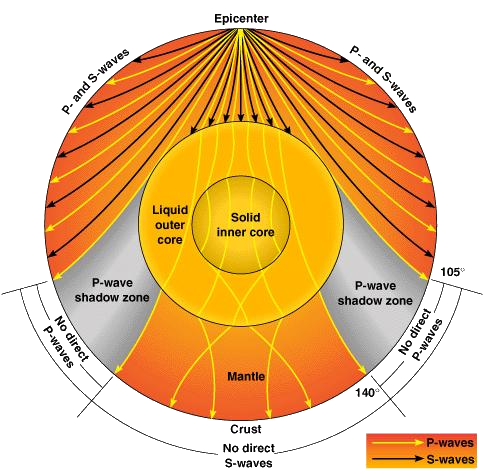
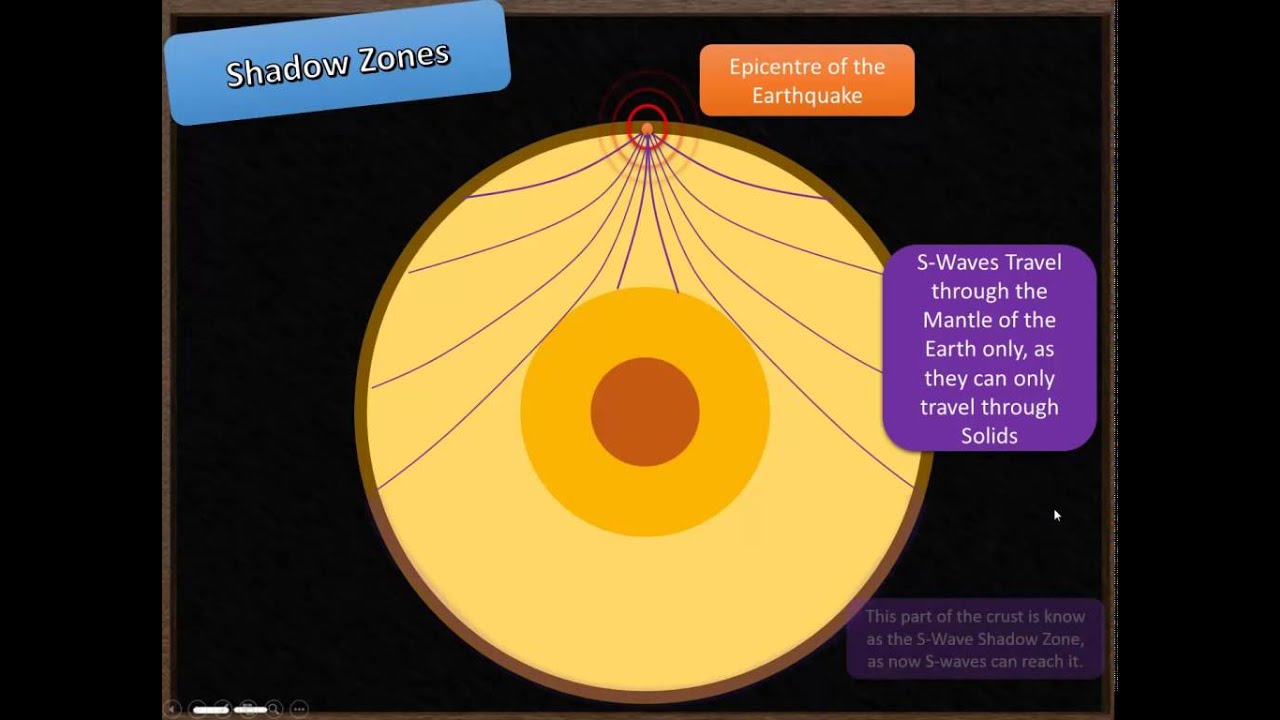
S wave shadow zone diagram. Travel the same speed but rise toward the surface. There is a large S-wave shadow zone (labelled " No direct S-waves" ) extending across the side of the globe opposite from the epicenter (from 105o ). H - object height, a - angle between Sun and horizon.
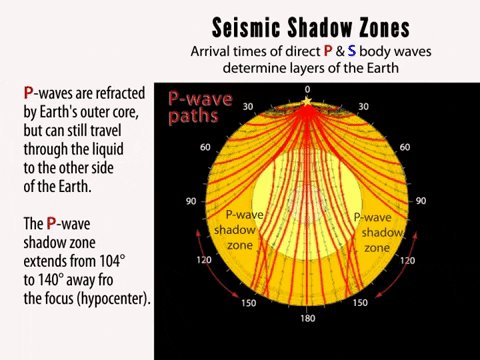
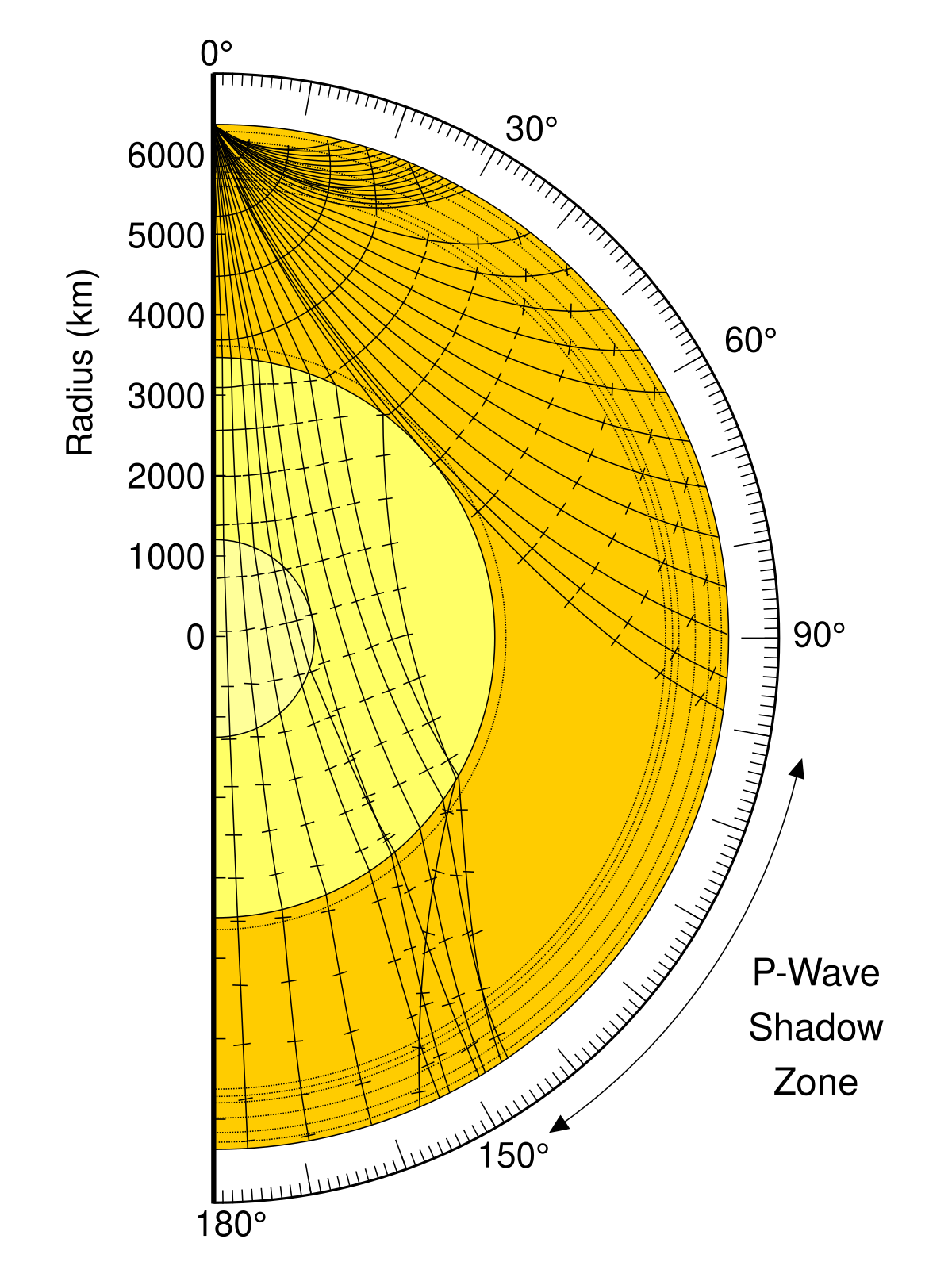
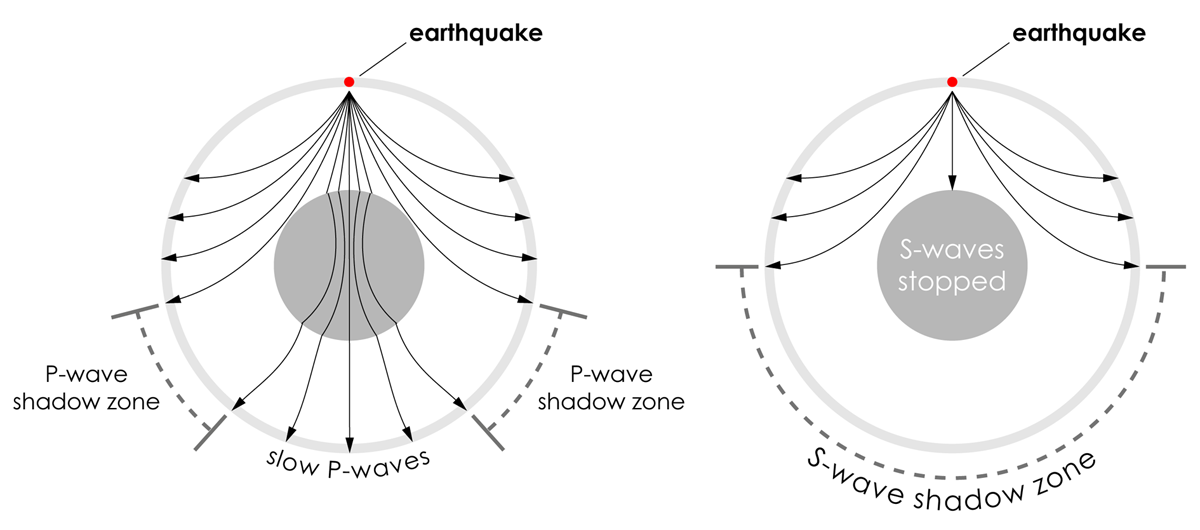
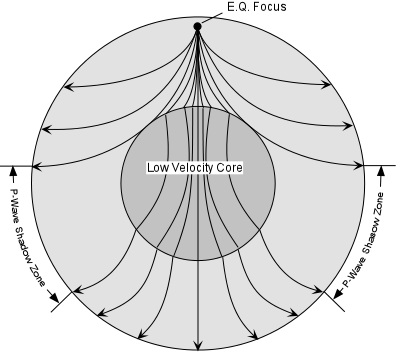
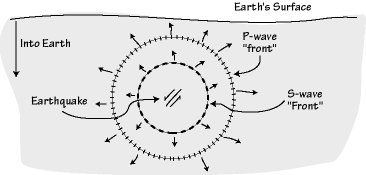
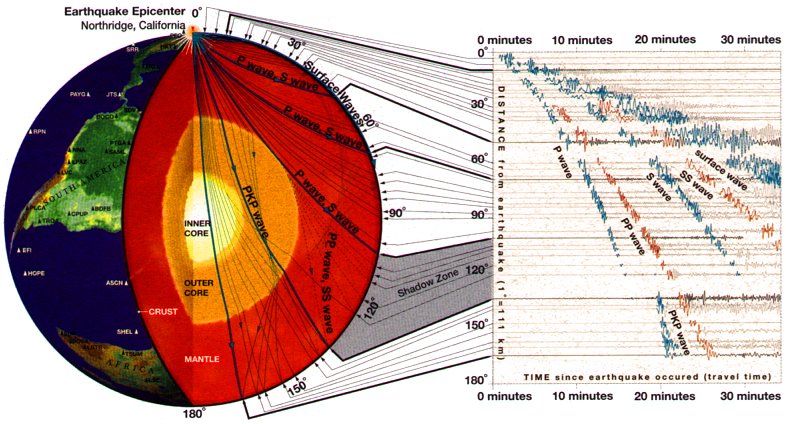
When an earthquake occurs, seismic waves radiate out spherically from the earthquake's focus.The primary seismic waves are refracted by the liquid outer core of the Earth and are not detected between 104° and 140° (between. The sound waves are being refracted upwards and will never reach the observer. The shadow zone results from S waves being stopped entirely by the liquid core and P wavesbeing bent (refracted) by the liquid core.
S waves, or secondary waves, are the second waves to arrive during an earthquake. The S wave shadow zone The S wave shadow zone is the area of the Earth’s surface where S waves are not detected following an earthquake. 30 Second-order Low velocity zones.
The S-wave shadow zone is evidence that:. Louie) You can get a rough estimate of the size of the Earth's core by simply assuming that the last S wave, before the shadow zone starts at 105 degrees, travels in a straight line. What happens to the p-waves when they encounter the boundary.
C) S-waves are only transmitted through solid media. What type of seismic wave is being recorded by the seismograph in the diagram?. It is this property of S waves that led seismologists to conclude that the Earth's outer core is a liquid.
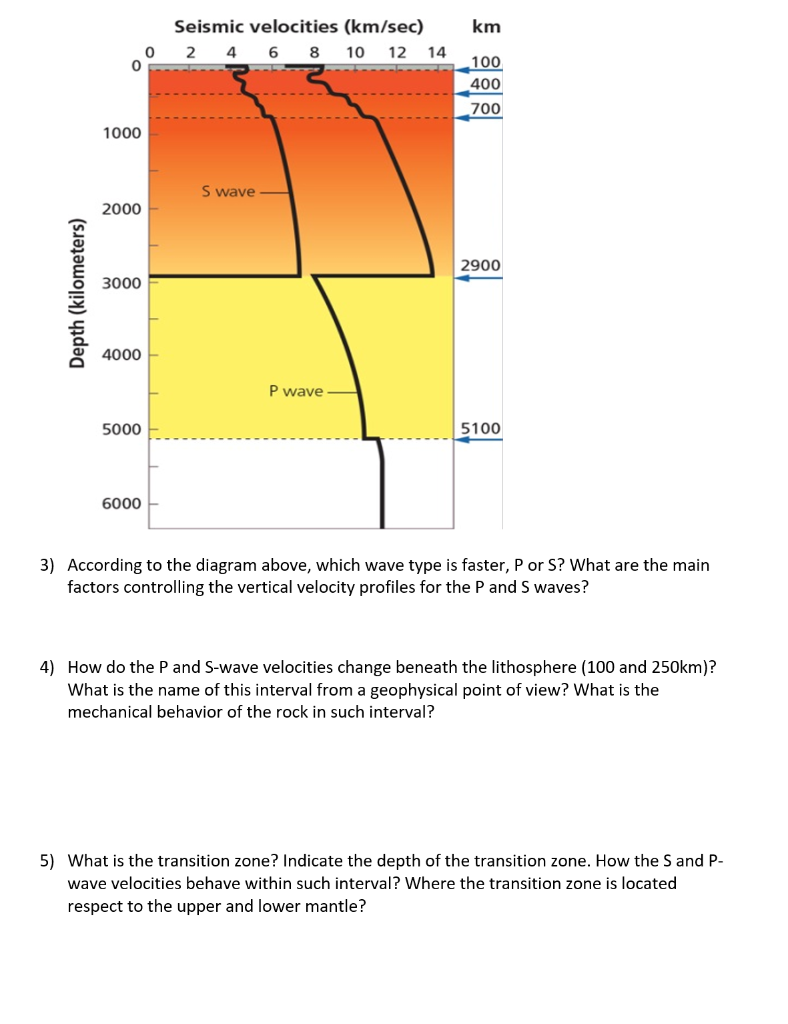
1) P-waves are absorbed and S-waves are refracted by the earth' outer core. The Transition Zone Abrupt changes in P-wave and S-wave velocities occur when the waves. The S wave shadow zone is caused by the outer core not transmitting S waves.
A person standing in the shadow zone will not hear the sound even though he/she might be able to see the source. An S wave is a transverse wave and travels slower than a P wave, thus arriving after the P wave. S waves do not travel through liquids—they are stopped at the CMB—and there is an S wave shadow on the side of Earth opposite a seismic source.
The shadow zone is an area of almost stagnant water sitting between the rising currents caused by the rough topography and geothermal heat sources below 2.5 km and the shallower wind driven. Diagram and indicate if they are solid or liquid. This produces a 'shadow zone' on certain parts of the Earth's surface where S-waves are not recorded, and this is used as the main piece of evidence to deduce the size of the core.
A) the Earth’s inner core is solid. 17 Layers of the Earth Earth’s CORE. Seismic shadow zones have taught us much about the inside of the earth.
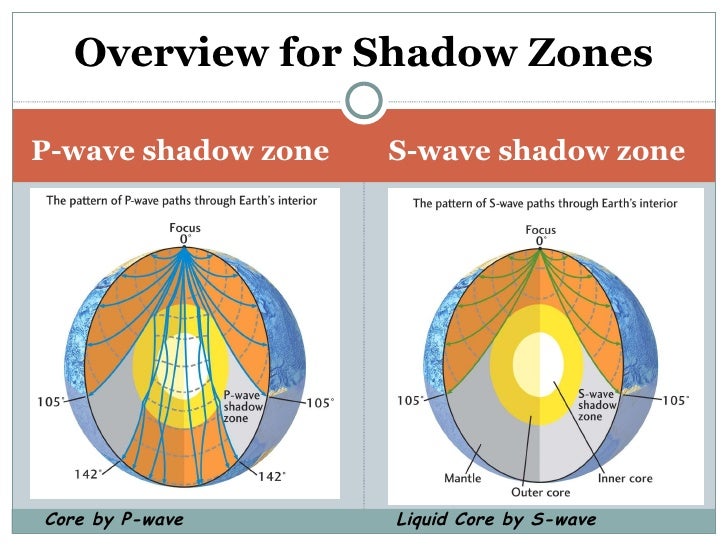
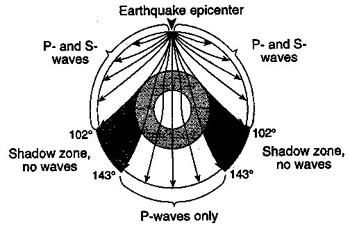
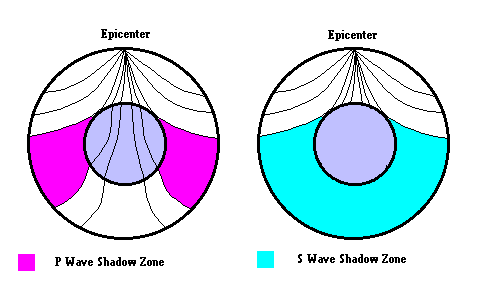
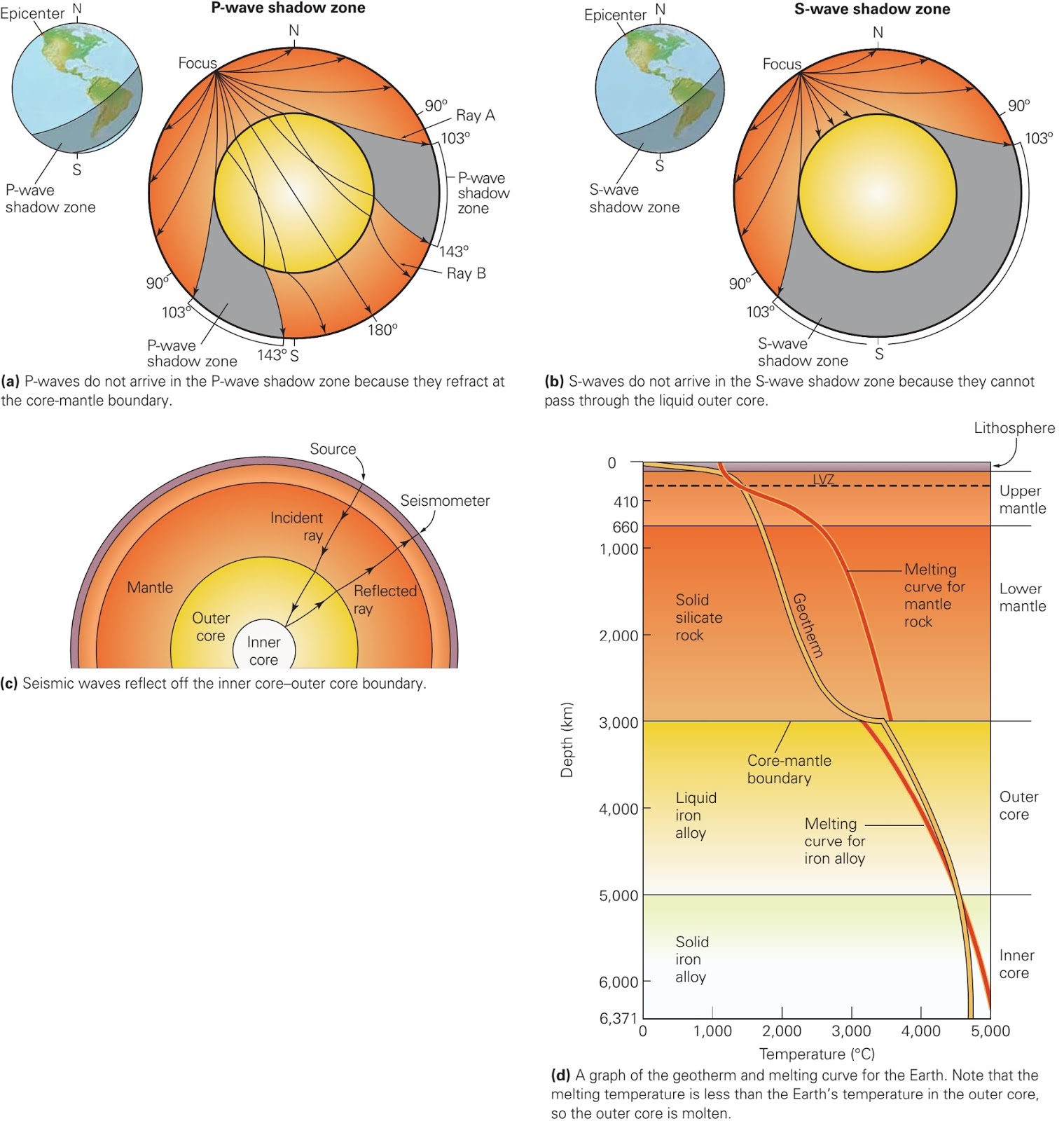
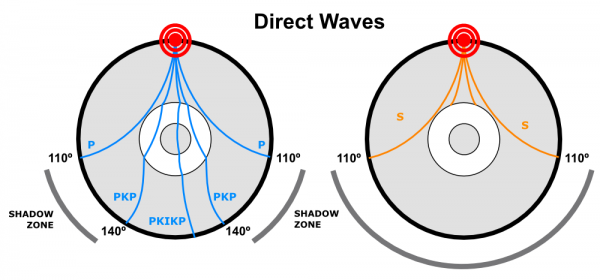
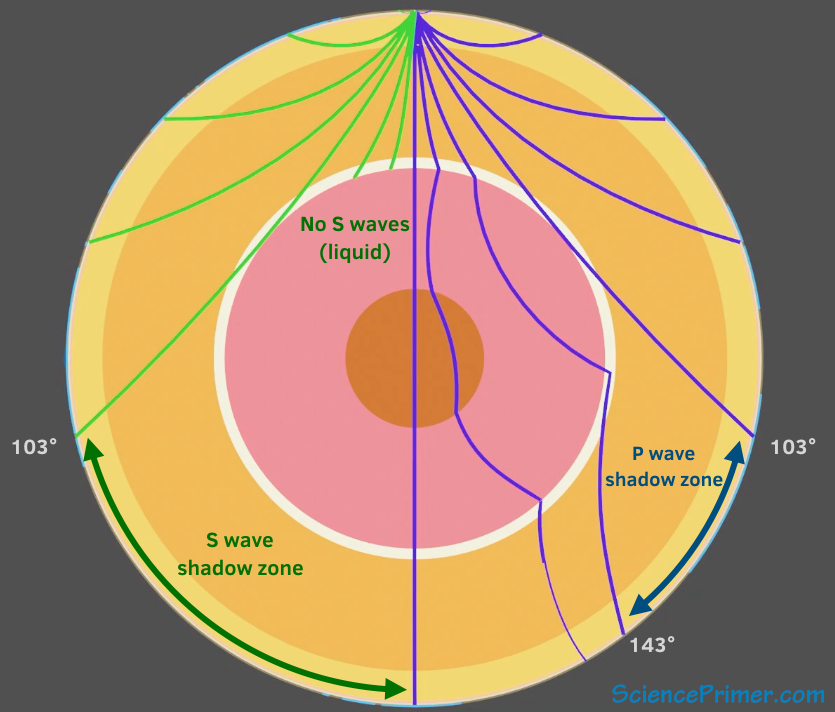
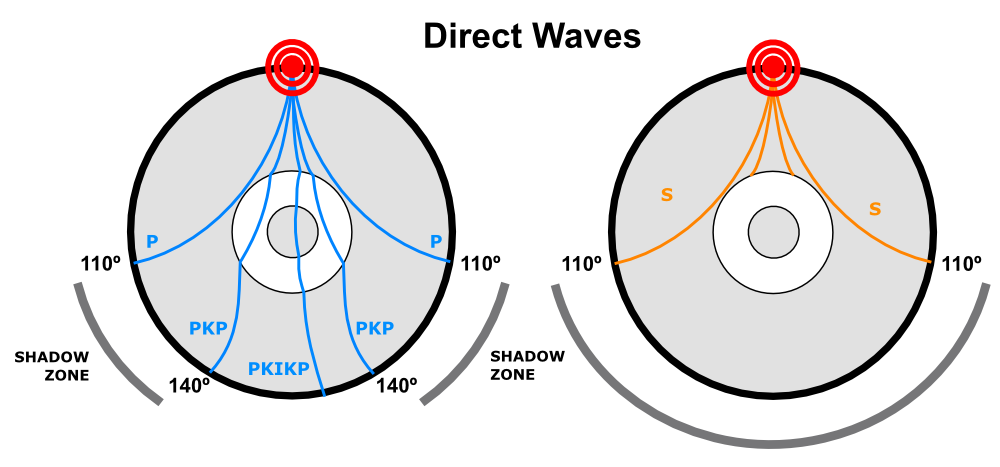
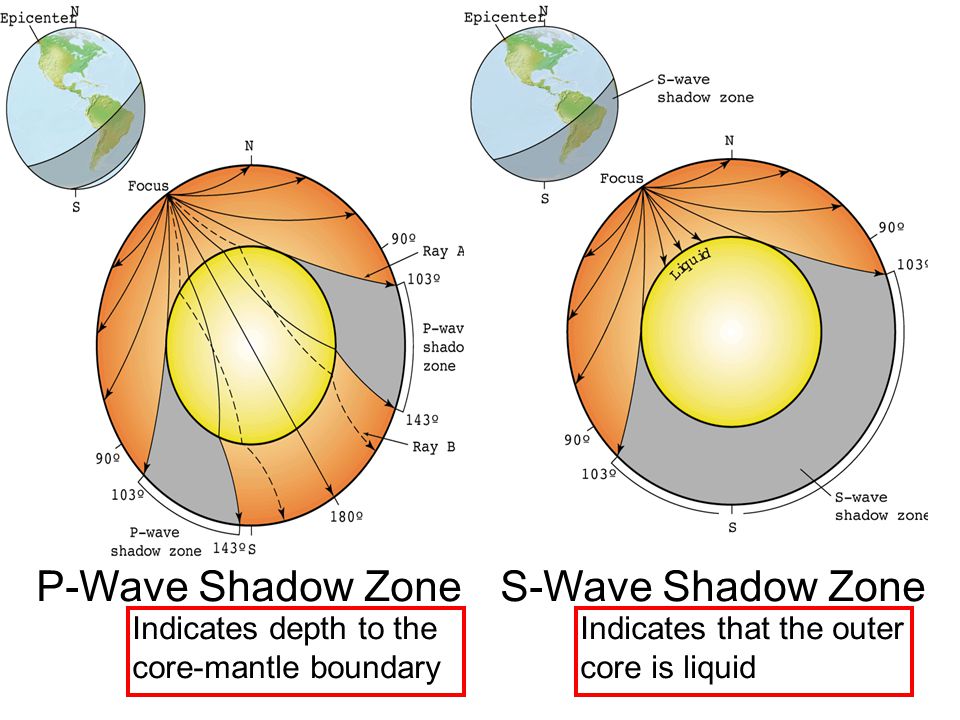
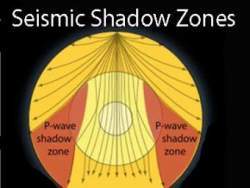
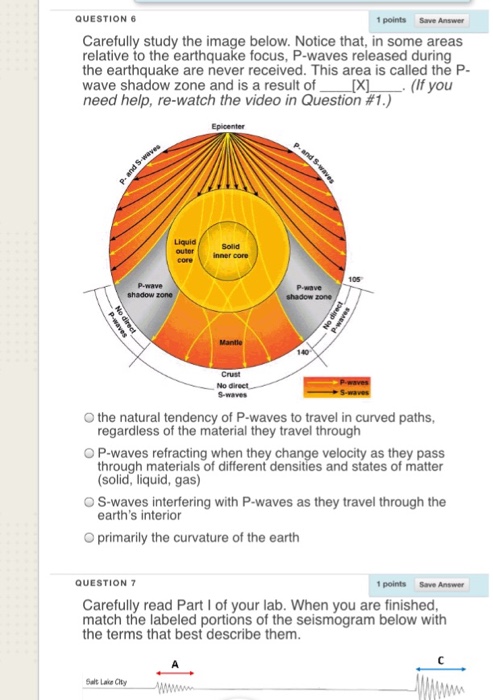
The shadow zone of P-waves appears as a band around the earth between 103° and 142° away from the. P-waves are converted to S-waves, which cannot travel through the core. S waves cause more damage,.
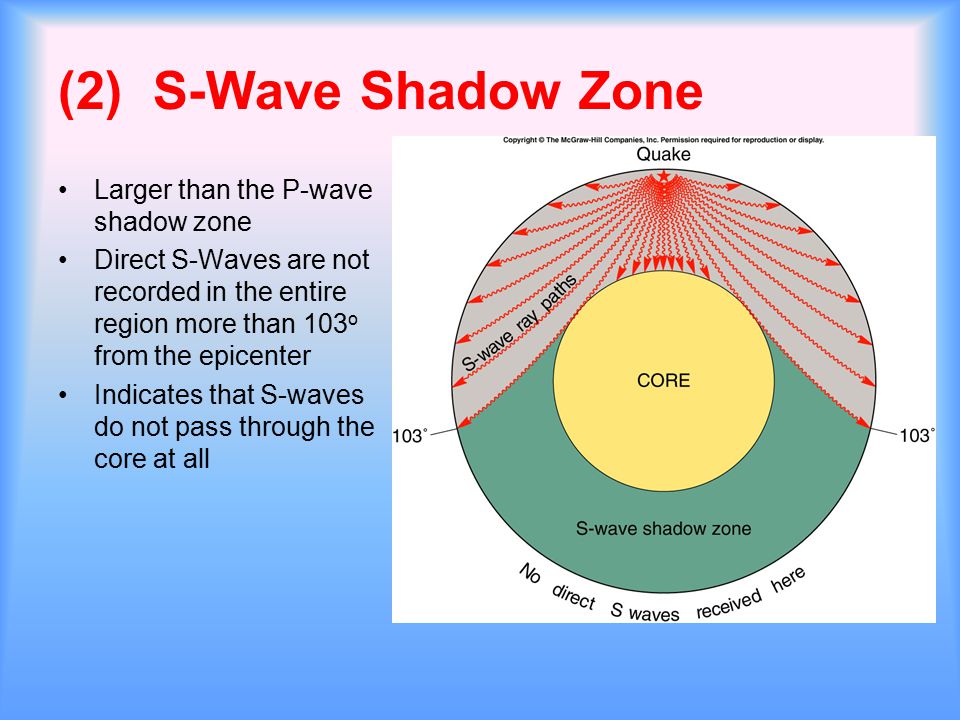
2) P-waves are refracted and S-waves are absorbed by the earth's outer core. S-wave shadow zone - caused by S-waves' inability to pass through liquid. The S-wave shadow zone is larger than the P-wave shadow zone.
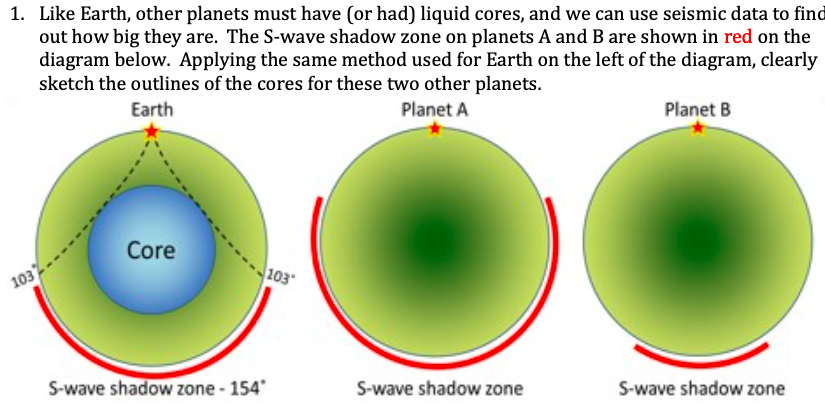
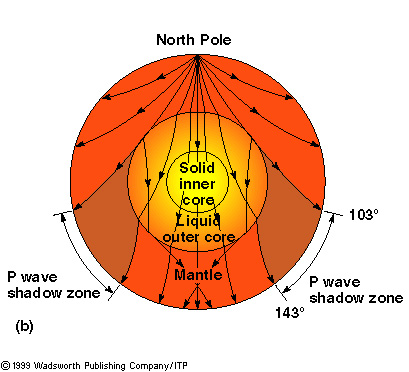
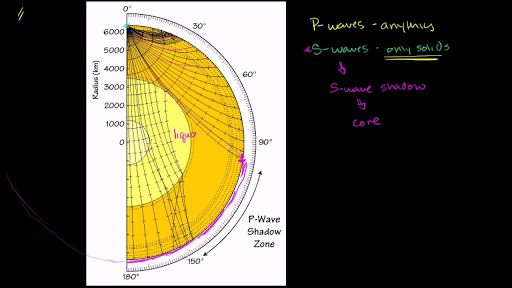
A seismic shadow zone is an area of the Earth's surface where seismographs can only barely detect an earthquake after its seismic waves have passed through the Earth. The P-wave shadow zone is 103-142 degrees and the S-wave shadow zone is 103-103 degrees. The core is made of iron and nickel.
It is after studying the trajectory of S waves through the layers of earth, scientists were able to conclude that the earth’s outer core is liquid. Through measuring how P and S waves travel through the earth and out the other side, a seismic wave shadow zone was discovered in about 1910. Three different S-wave phases show how the initial S wave is stopped (damped), or how it changes when encountering boundaries in the Earth.
What is a P or S wave “shadow zone” on the opposite side of the Earth from an earthquake?. Scientists deduced the structure of Earth's interior and how waves move through it by analyzing thousands of earthquakes recorded at Earth's surface. Sketch the layers on your diagram.
Another important property of an S-wave is its inability to pass through liquids. Match the letter on the diagram with the appropriate description:. 9 Observe the path taken by P and S waves on Earth.
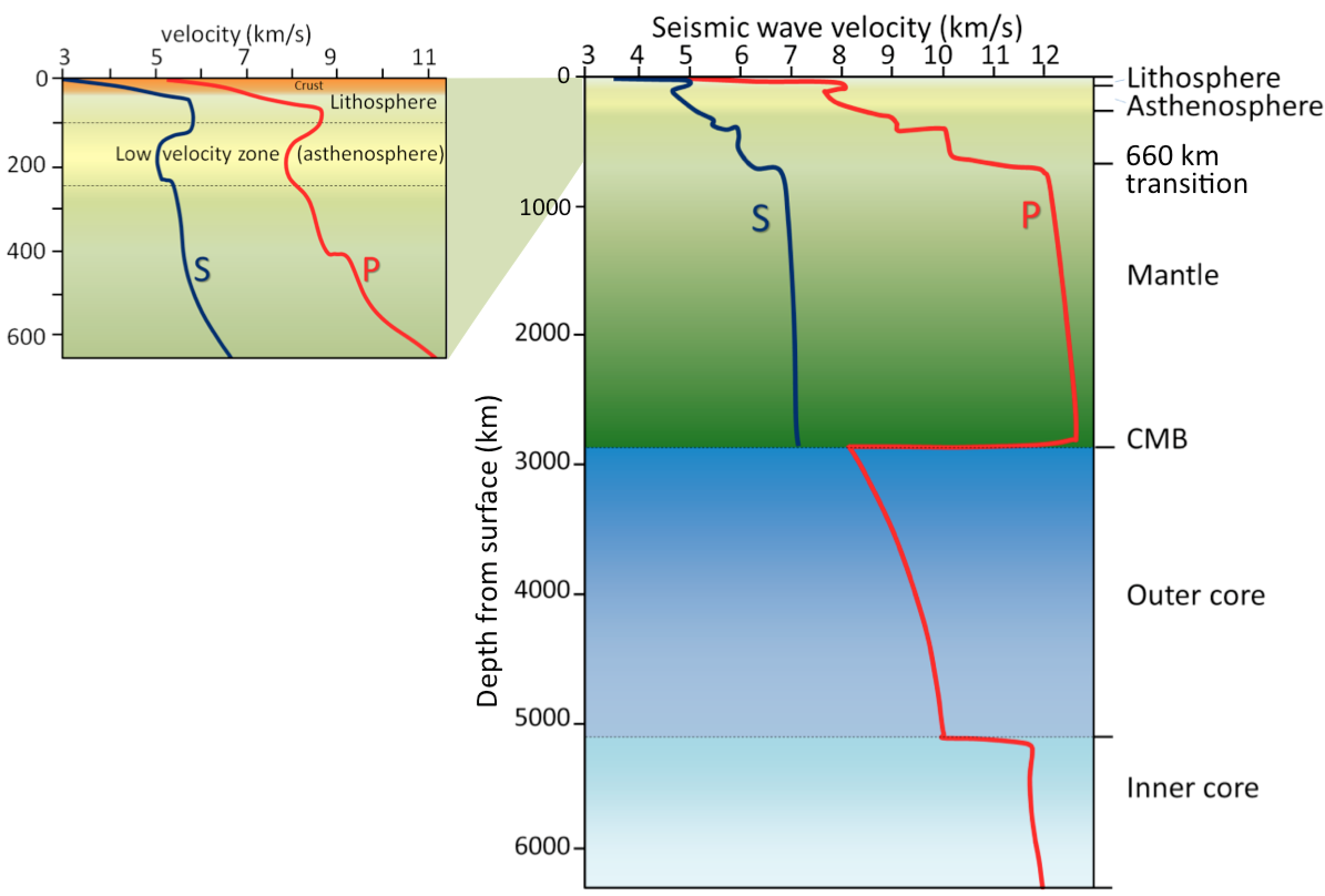
(1) Complexity with Low Velocity Zones First-order Low velocity Zones. A) The outer core is liquid. B) The outer core is composed of iron and nickel oxides.
This simple online calculator gives a vertical object shadow length for specified day and geographic coordinate. As a result, the wave changes direction and bends upwards. S-wave shadow zone P-wave shadow zone - caused by refraction of seismic waves.
Honda ANF125 Wave 125 Electrical Wiring Harness Diagram Schematic HERE. The area where P and S waves do not arrive is called the shadow zone. S-waves cannot travel through the molten (liquid) outer core.
S-waves shadow zone means the area of the Earth from angular distances. P-wave can travel through solid , liquid and air, so the P-wave turns or refracts when it hits the liquid outer core, and although it still comes out, it does not. A) A P wave b) An S wave c) A surface wave d) All of the above.
S waves move rock particles up and down, or side-to-side--perpendicular to the direction that the wave is traveling in (the direction of wave propagation). Now this area is different for different epicenter and shadow zone extent of P and S waves are also different owing to their differences. They are much slower than P waves and can travel only through solids.
S wave shadow zone is caused by the fact no shear wave propagates through the outer core, which is liquid. The bending, called diffraction, results in a change of direction of part of the wave energy from the normal line-of-sight path. The entire zone beyond 103° does not receive S-waves, and hence this zone is identified as the shadow zone of S-waves.
A shadow zone occurs because the density of the earth does not increase or decrease gradually with depth all the way to the center. The calculator uses Sun position algorithm to calculate sun altitude. The refracted wave shown in the diagram has passed into a material that caused it to:.
Since the outer core is fluid, and S-waves cannot travel through a fluid, the "S-wave shadow zone" is even larger, extending from about 100° to 180°. He recognized that the P-wave shadow zone was due to the refraction and reflection of primary waves by the Earth's molten core. Draw a diagram illustrating the difference between the.
P waves travel faster in a push-pull pattern while the slower S waves travel in an up-down pattern. There are 2 different types of shadow zones (areas where these waves relative to the epicenter of the Earthquake. The shadow zone also defined the diameter of the core.
When an s. The shadow zone results from S waves being stopped entirely by the liquid core. Estimate the radius of the outer core.
Lectures by Walter Lewin. The shadow zone is the area of the earth from angular distances of 104 to 140 degrees from a given earthquake that does not receive any direct P waves. Honda C50 Super Cub Electrical Wiring Harness Diagram Schematic HERE.
Do not receive any waves — these areas are in the shadow zone of this simulated earthquake. B) The Earth’s outer core is liquid. Honda C70 Cub Electrical Harness Wiring Diagram Schematic 1971 - 1984 HERE.
Describe the differences between P and S waves. 16 Seismology and Earth structure. Honda C65 Cub Electrical Harness Wiring Diagram Schematic 1964 - 1970 HERE.
S wave -- a shadow zone appears when the velocity suddenly decreases 103-180 degrees from the epicenter. Label both the p-wave and the s-wave shadow zones in the diagram above. The core has a radius of 3470 km.
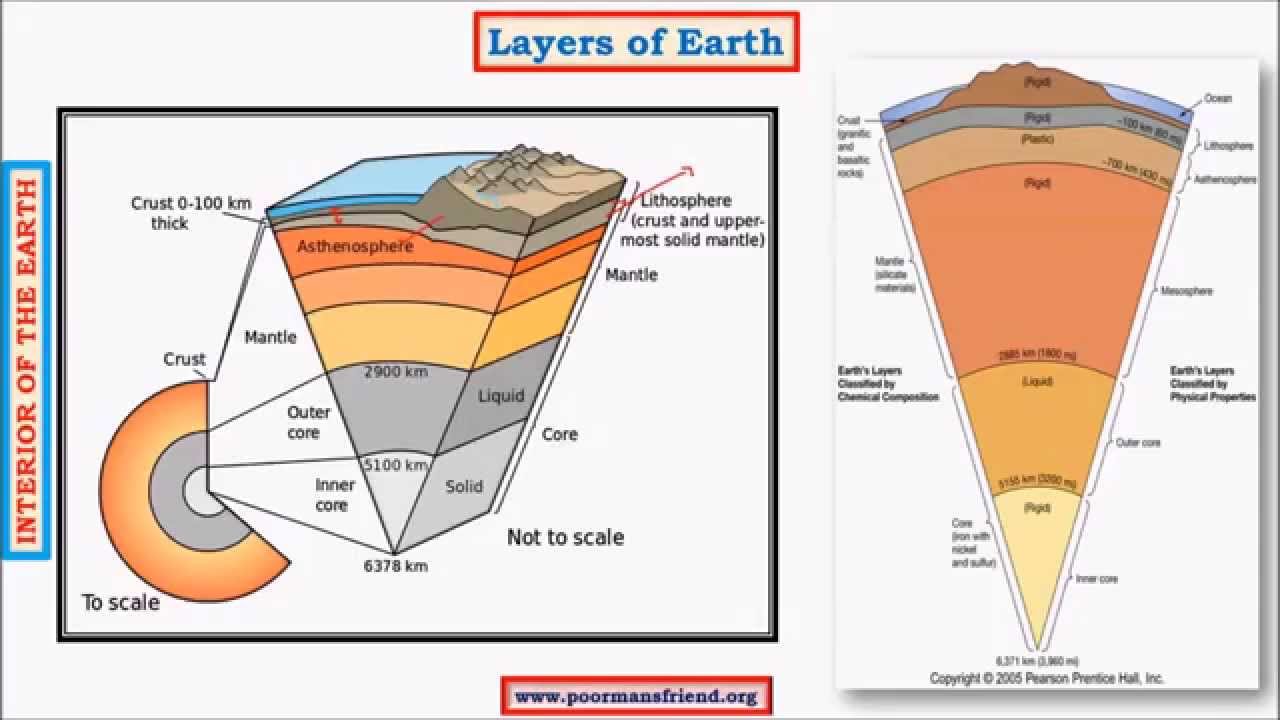
INTRODUCTION TO PETROLOGY 14 29 40. Sun altitude and shadow. Earth's Internal Structure We have already discussed the main elements in Earth's interior, the core, the mantle, and the crust.
S-wave travels only through solid and when it gets into the liquid zone it just stops so on the other side of the earth, there are no waves, which causes the S-wave shadow zone. The shadow zone on the opposite side of Earth receive only Pwaves. • There is a smaller P-wave shadow zone, seen on both sides (gray shading), from 105o to 140o.
• Note the shadow zones. 41 – An S-wave shadow zone exists because _____. Draw a diagram or write a description to explain how data from seismic waves disproves.
The Earth has to have a molten, fluid core to explain the lack of S waves in the shadow zone, and the bending of P waves to form their shadow zone. Examine the frames near the end of the animation to identify the areas where no P or S waves are received. They will make you ♥ Physics.
These diagram are helpful with visualizing this. D) a and b e) b and c 42. The shadow zone results from S waves being stopped entirely by the liquid core.
The mantle behaves as ductile material. Match the major Earth boundary with the appropriate description:. P waves are on the side and S waves are in the middle.
For each item below, use. S-waves do not travel through liquids (they are attenuated). This observation led to the discovery of the liquid outer core.
Seismic waves follow straight paths through the interior of the Earth. A radio wave that meets an obstacle has a natural tendency to bend around the obstacle as illustrated in the figure. This can create a "shadow zone" region into which the sound wave cannot penetrate.
The inner core is solid. From the lack of S waves and a great slowing of the P wave velocity (by about 40%) it was deduced that the outer core is made of liquid. It crosses an arc of 105 degrees on the Earth (see the diagram on the left).
S waves can only travel through solids, and as a result do not travel through the liquid core of. Honda C50M C 50 Electrical Wiring Harness Diagram Schematic HERE. The angular distance from the seismic source to the shadow zone is 103° on either side, so the total angular distance of the shadow zone is 154°.
Three different S-wave phases show how the initial S wave is stopped (damped), or how it changes when encountering boundaries in the Earth. A major zone of active volcanoes that encircles the Pacific Ocean. S waves only travel through solids.
Some of the wave energy reflects off the boundary between the mantle and core. No P-waves or S-waves are received in the shadow zone because;. Using the pulldown boxes, match each item on the left to the corresponding item at right.
P wave shadow zone is caused by a decrease of P speed in the outer core. Shadow zone is a particular area formed on earth surface during an earthquake where P and S wave cannot reach. In the year 1913, Gutenberg proved the existence of the Earth's core.
Layers of the Earth. What property(ies) of rock determines the seismic wave velocity through it?. The outer core is fluid.
This shadow zone has led geologists to a model of the Earth. Www.iris.edu/earthquake for more animations. All of the above:.
Play the animation again. The cause of the P-wave shadow zone includes:. 3-4 Building on strong and safe foundations 3 foundation design loads 3.2.2 Design Stillwater Flood Depth (ds) Design stillwater flood depth (d s) is the vertical distance between the eroded ground elevation and the stillwater flood elevation associated with the design flood.
A diagram of a cross-section of the Earth shows how the epicenter of an earthquake, the earthquakes S-shadow and the center of the inner core can be used to estimate the radius of the Earth's core. The S-wave shadow zone is evidence that. After an earthquake, most Richter scales around the globe can detect P-waves, but less are.
He also found that the S-wave shadow zone resulted from the complete absorbtion of the secondary waves by the liquid core. Then it uses this formula to calculate shadow length:, where. With increasing diameter of a liquid layer, the size of the S wave shadow zone becomes larger.
S-waves are not transmitted through the liquid outer core. A) and b) e) a) and c) 43 – The Richter scale classifies an earthquake according to its _____ which is a. P waves travel through all materials;.
Was inspired by Halley s idea. Differences between P and S waves include wave speeds, types and sizes and travel capabilities. The name secondary wave comes from the fact that they are the second type of wave to be detected by an earthquake seismogram, after the compressional primary wave, or P-wave, because S-waves travel slower in rock.Unlike P-waves, S-waves cannot travel through the molten outer core of the Earth, and this causes a shadow zone for S-waves opposite to their origin.
A triangle is drawn from the three points so the radius of the Earth is equal to the length of two sides of the triangle. The radius of the entire Earth is 6370 km. What type of seismic wave is being recorded by the seismograph in the diagram?.
8 What happens to the size of the S wave shadow zone as the diameter of the liquid layer increases?.

Which Country Has A Shadow Zone Area Where Earthquake Does Not Occur Quora

Evidence For Earth S Layers 8th Grade Science

A Conceptual Magmatic Bodies Shown With Location Of S Wave Shadow Download Scientific Diagram
S Wave Shadow Zone Diagram のギャラリー
3 2 Imaging Earth S Interior Physical Geology First University Of Saskatchewan Edition
Http Geoscience Msc Sa Edu Au Library 2 1 earths crust and interior Pdf
Seismic Shadow Zones S Wave Shadow Zone Incorporated Research Institutions For Seismology

Shake Bake

Seismic Shadow Zone Definition Overview Study Com

Details Of The Core Not Well Established And Still Open To Revision See Recent Paper By Price On Fe In The Core
Oncel Akademi Solid Earth Geophysics
Earthquakes And Plate Tectonics
Thread By Iris Epo Seismic Shadow Zone How Do P S Waves Give Evidence For A Liquid Outer Core Thread Iris Edu Hq Inclass Ani Earthquake Seismology Data
Shadow Zone Wikipedia
Earthquakes
Solved Like Earth Other Planets Must Have Or Had Liqui Chegg Com

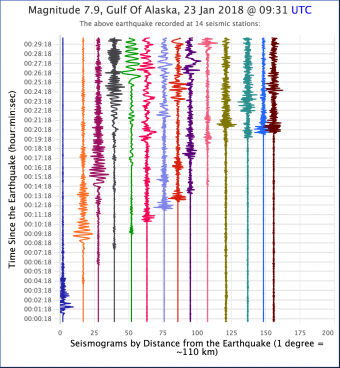
How Do I Read A Seismogram

Earthquakes Happen Every Day Every Hour Somewhere In The World 95 Of Seismicity In Hawaii Is Due To Volcanism Ppt Download
What Is A Shadow Zone During An Earthquake Quora
Seismic Shadow Zones S Wave Shadow Zone Incorporated Research Institutions For Seismology

Diagram Critical Paths Of Seismic Waves Sent Out From An Earthquake Focus O In Relation To The Core Boundary And The Shadow Zone

Why Are Seismic Waves Not Detected Within The Shadow Zone Quora
Where Did We Get Our Evidence About The Earth S Structure Socratic

Earth Quakes Ppt Video Online Download
Waves As Probes
Seismic Study Of Earth S Interior Learning Geology
Earthquakes

P Wave Wikipedia
Why Do Earthquake Waves Develop Shadow Zone Askscience
We Have A Seismometer In Our Basement Highly Allochthonous

9 1 Understanding Earth Through Seismology Physical Geology
Smart Study Zone Types Of Earthquake Seismic Waves In English

Introduction To Physical Geology Syllabus
Http Www3 Nd Edu Cneal Planetearth Chapt 10 Marshak Pdf
Q Tbn 3aand9gcretgtubtu2ucurxz38ueto8y7kleutgamtqk9ysd8azltege5g Usqp Cau

The Earth Story S Wave Shadow Zone From And Early Age We Are
2
Seimic Waves And Earth S Interior
How We Know About The Earth S Core Video Khan Academy

Waiting For The Hollow Earth What To Expect When You Re Expecting Inner Earth Relatives An American In Bosnia

1 Sketch And Describe P And S Wave Shadow Zones Chegg Com

Layered Structure Earth Crust Mantle Metal Inner Outer Core Iron Nickel S P Earthquake Waves Shadow Zones Geology Earth Gcse Science Revision Notes

Chapter 8 Flashcards Quizlet
Http Www Soest Hawaii Edu Oceanography Courses Html Ocn1 Instructors Ferron Ocn1 L5 Earth structure Pdf
How Do Scientists Use Seismic Waves To Map The Earth S Interior Socratic

My Favorite Demonstration The P Wave Shadow Zone Shedding Light On The Concept

Seismic Shadow Zone Definition Overview Study Com
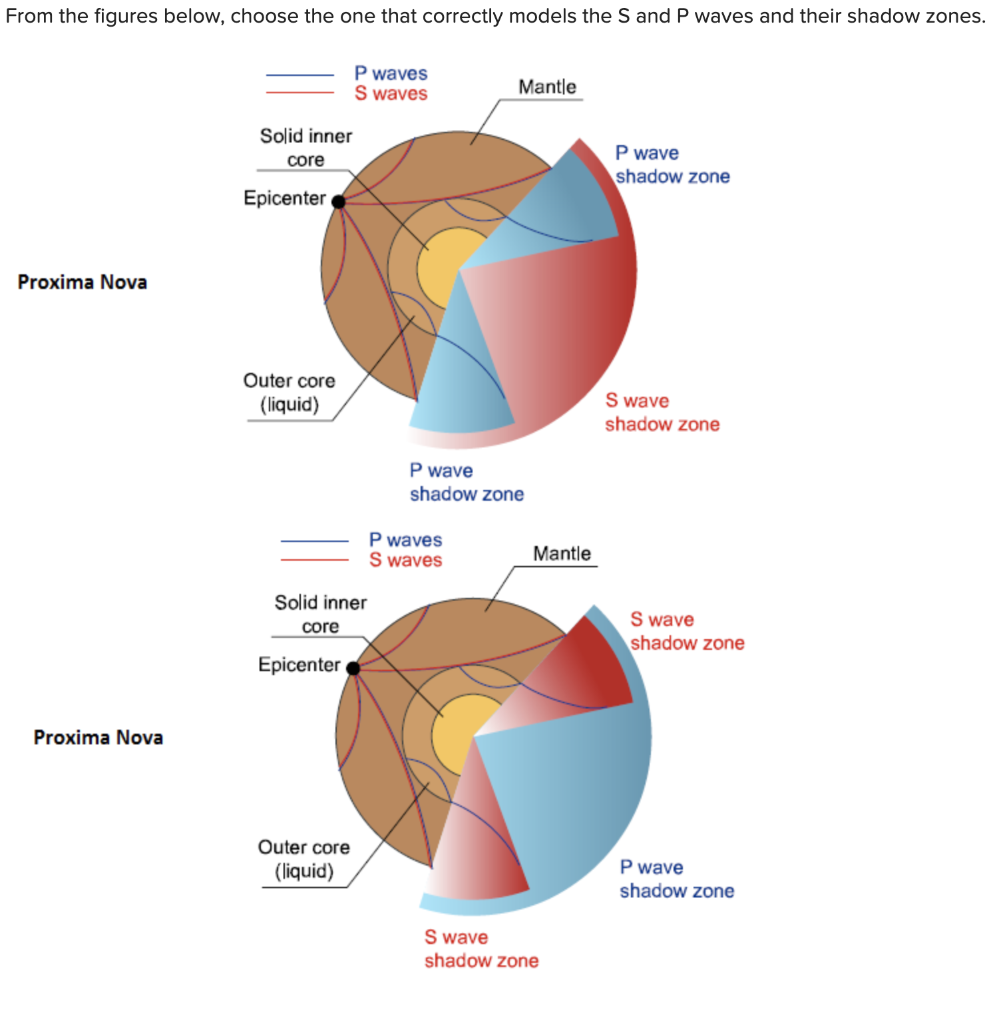
Solved Click To Select V Is The Correct Model Of The S Chegg Com

A Seismic Shadow Zone Best Ias Ukpsc Coaching In Dehradun
Seismic Shadow Zones S Wave Shadow Zone Incorporated Research Institutions For Seismology

Earthquakes And The Interior Earthquakes Are Definitely A Geologic Hazard For People Living In Earthquake Regions But The Seismic Waves Generated By Ppt Download
Earthquakes

A Simple Diagram That Illustrates The Shadow Zone For An Assumed Download Scientific Diagram
Geophysical Properties Ppt Video Online Download

Introduction To Earthquakes Vocabulary Seismic Waves Help Reveal The Structure Of Earth S Interior Diagram Quizlet
How Earthquakes Show Us The Inside Of The Earth Science Primer

Layered Structure Earth Crust Mantle Metal Inner Outer Core Iron Nickel S P Earthquake Waves Shadow Zones Geology Earth Gcse Science Revision Notes
Solved 1 Sketch And Describe P And S Wave Shadow Zones Chegg Com
Seismic Waves Shadow Zone Of P Waves And S Waves Pmf Ias
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/3691396/FG15_26.0.JPG)
How Inge Lehmann Used Earthquakes To Discover The Earth S Inner Core Vox
Direct Waves Highly Allochthonous
G4 Earth S Interior Upsc Ias Shadow Zone Of S P Waves Crust Core Mantle Earth S Crust Youtube

Seismic Shadow Zones Introduction To P S Wave Shadow Zones Educational Youtube

Earthquakes Ppt

Seismology And The Earth
Lecture 09 Earthquakes P 6
Earthquake Waves Body And Surface Waves And Concept Of Shadow Zone Issues And Analysis Abhipedia Powered By Abhimanu Ias
D32ogoqmya1dw8 Cloudfront Net Files Angle Educational Materials Activities Human Wave Modeling P Pdf
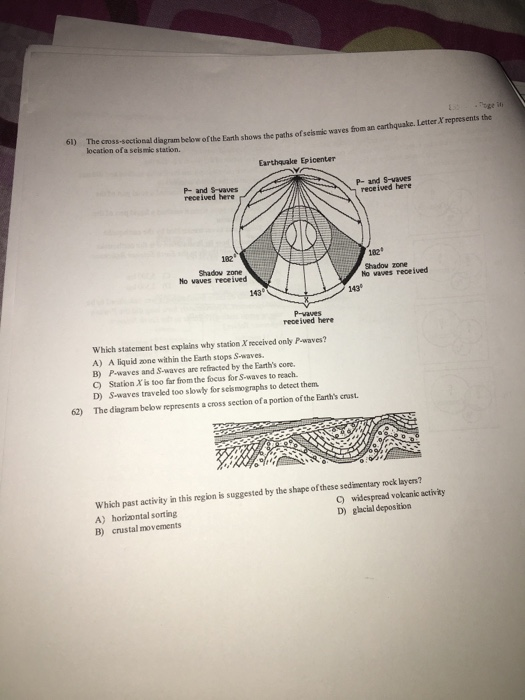
Solved 61 The Cross Soctional Diagram Below Of The Earth Chegg Com

Seismic Waves As Probes Solid Earth Spu30x Courseware Edx Earth Science Lessons Seismic Wave Earth Science

Chapter 7 Section 3
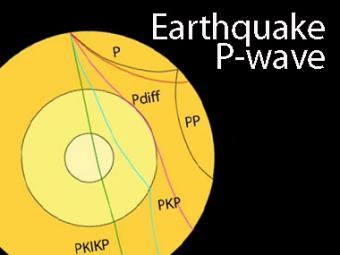
Seismic Shadow Zones P Wave Incorporated Research Institutions For Seismology

March 29 1936 Notes On Earth S Inner Core Earth Magazine

Seismic Waves Shadow Zone Of P Waves And S Waves Pmf Ias

Seismic Phases P Wave Shadow Zone Youtube
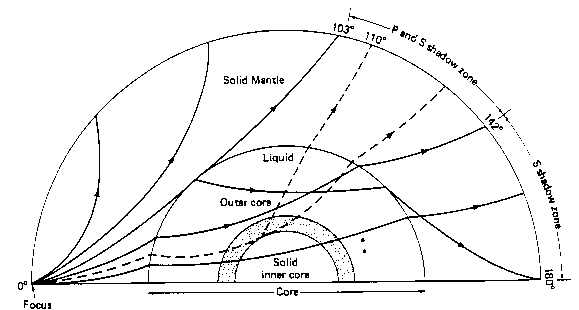
Ocean 540 Geologic Overview
Seismic Waves Earth S Structure
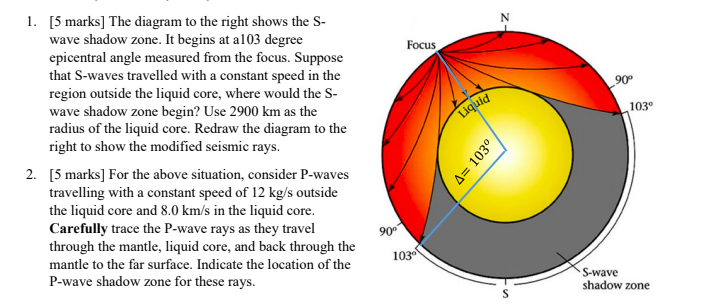
Focus 1 5 Marks The Diagram To The Right Shows Chegg Com

Earthquake Shadows Earth Science Ck 12 Plix Series
3 2 Imaging Earth S Interior Physical Geology First University Of Saskatchewan Edition

My Favorite Demonstration The P Wave Shadow Zone Shedding Light On The Concept
2

Unacademy For Upsc Geography Series 4
Seismic Profiles Of Earth S Interior Ppt Video Online Download
Seismic Shadow Zone Basic Introduction Incorporated Research Institutions For Seismology

Tectonics Lecture 3 Internal Composition Of Earth Flashcards Quizlet
Solved Carefully Study The Image Below Notice That In S Chegg Com
P1 Earthquake Shadow Zones Youtube

Geology 105h Exam 1 Flashcards Quizlet
Iris Educational Materials

3 Shadow Zone Caused By S Waves Not Passing Through Liquid Outer Core Seismic Wave Seismic Education

Shadow Zones Mechanical Wave Earth Science Outer Core

Details Of The Core Not Well Established And Still Open To Revision See Recent Paper By Price On Fe In The Core
Http Www Soest Hawaii Edu Gg Faculty Popp Oct07 Ch 12 Pdf
Solved 1 Like Earth Other Planets Must Have Or Had Li Chegg Com

5 A Cross Section Of The Earth With Earthquake Wave Paths Defined And Download Scientific Diagram
Multiple Choice

Earth Sci Eq Flashcards Quizlet
Earthquakes

Evidence For Earth S Layers 8th Grade Science

Seismic Waves Surface Waves Seismic Waves Are Shock Waves Given Off By Earthquakes There Are 2 Types 1 Body Waves Originate From The Focus F Travel Ppt Download
What Is A Shadow Zone During An Earthquake Quora



